Minimization of DFA in Hindi (Minimization of Automata Machines)
Unit 2
Types of Finite Automata
Topic 4 : Minimization of DFA in hindi (Minimization of Automata Machines)
Automata theory (Theory Computer की एक Branch) में, DFA Minimization एक दिए गए Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA) (DFA) को एक समान DFA में बदलने का कार्य है जिसमें States की Minimizationसंख्या होती है। यहां दो DFA को समान कहा जाता है यदि वे एक ही Regular Language को पहचानते हैं। इस कार्य को पूरा करने वाले कई अलग-अलग algorithm Automata theory पर standard textbooks में known और described हैं
प्रत्येक Regular Language के लिए, एक minimal automaton भी मौजूद होता है जो इसे Accept करता है, अर्थात, एक DFA जिसमें Minimum Number में State होते हैं और यह DFA Unique होता है | Minimum DFA pattern matching जैसे कार्यों के लिए Minimum computational लागत सुनिश्चित करता है।
States के दो वर्ग हैं जिन्हें Language को प्रभावित किए बिना मूल DFA से Removedया Merged किया जा सकता है, इसे कम से कम करना स्वीकार करता है।
-
Unreachable states वे State हैं जो किसी input String के लिए DFA की initial state से उपलब्ध नहीं हैं।
-
Nondistinguishable state वे होते हैं जिन्हें किसी भी input string के लिए एक दूसरे से अलग नहीं किया जा सकता है।
DFA minimization आमतौर पर 3 Step में किया जाता है, relevant States को Removed या merged करने के लिए। चूंकि nondistinguishable States का Elimination computational रूप से सबसे महंगा है, इसलिए इसे आमतौर पर last step के रूप में किया जाता है।
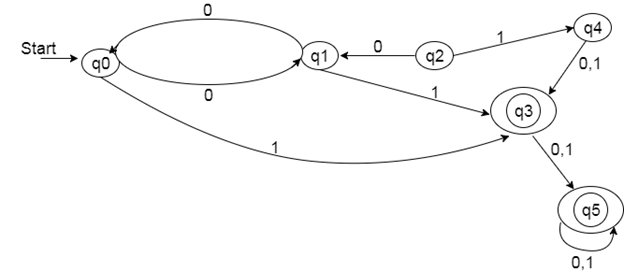
Solution:
Step 1 : दिए गए DFA में, q2 और q4 unreachable states हैं, इसलिए उन्हें Remove कर दें।
Step 2 : बाकी States के लिए transition table बनाएं।
| State | 0 | 1 | |
| →q0 |
|
q3 | |
| q1 |
|
q3 | |
| *q3 |
|
q5 | |
| *q5 |
|
q5 |
Step 3 : अब transition table की rows को दो sets में divide करें
1. एक set में वे rows होती हैं, जो non-final states से शुरू होती हैं
| State | 0 | 1 | |
| q0 | q1 |
|
|
| q1 | q0 |
|
2. एक other set में वे rows होती हैं, जो Final State से शुरू होती हैं।
| State | 0 | 1 |
| q3 | q5 | q5 |
| q5 | q5 | q5 |
Step 4: Set 1 में समान rows नहीं हैं, इसलिए set 1 समान होगा।
Step 5: Set 2 में, row 1 और row 2 q3 और q5 के समान है क्योंकि 0 और 1. एक ही state में transit करते हैं और इसलिए q5 को छोड़ दें और फिर बाकी में q5 को skip करें।
| State | 0 | 1 |
| q3 | q3 | q3 |
Step 6: अब Set 1 को set करें और 2 को set करें
| State | 0 | 1 |
| →q0 | q1 | q3 |
| q1 | q0 | q3 |
| *q3 | q3 | q3 |
Related Post
- What is Automata machine in hindi | Examples of automata machines
- Finite Automata as a language acceptor and translator | Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) | Nondeterministic Finite Automata(NFA) in Hindi
- What is Moore machines and mealy machines in Hindi
- What is Turing machine (composite machine) in toc in hindi
- Conversion from Mealy to Moore and vice versa in Hindi
- Non Deterministic Finite Automata in Hindi (NDFA)
- Deterministic Finite Automaton in Hindi (DFA) | Deterministic Finite-State Machine (DFSM)
- Conversion of NDFA to DFA in Hindi
- Minimization of DFA in Hindi (Minimization of Automata Machines)
- Regular Expression in TOC in Hindi
- Arden's Theorem in TOC in Hindi
- Union process in DFA | What is Union process in TOC
- Intersection of Finite Automata in Hindi
- Properties of Context Free Languages Hindi
- Two-way Deterministic Finite Automaton (2DFA) in Hindi
- Types of Grammar in TOC in Hindi | Chomsky Hierarchy in Theory of Computation
- Derivation Tree in TOC in Hindi
- Ambiguity in Grammar in TOC in Hindi
- Simplification of context free grammar in Hindi
- Conversion of grammar to automata machine and vice versa in Hindi
- Chomsky normal form and Greibach normal form in hindi
- What is Pushdown Automata in TOC in Hindi
- Example of PDA in Hindi | Example of Pushdown Automata in Hindi
- Deterministic pushdown automaton And Non-Deterministic pushdown automaton in Hindi
- Conversion of PDA Into Context Free Grammar and Vice Versa | PDA in TOC in hindi | Push Down Automata in Hindi | Context Free Grammar in Hindi
- CFG equivalent to PDA in hindi | context free grammar equivalent to push down automata in hindi | toc tutorial in hindi | theory of computation in hindi
- Petri Net Model in Hindi | Theory of Computation (TOC) Explained
- Techniques for Turing Machine Construction in Hindi
- Universal Turing Machine and Multitape in Hindi
- Multihead Turing Machine और Multidimensional Turing Machine की विशेषताएँ और अंतर
- NP Complete Problem in Hindi